What Characteristics does a Great Childcare Teacher Have?
A great childcare teacher possesses a unique set of characteristics and qualities that enable them to provide exceptional care and support for young children.
Check out our list of some of the key things we look for when we are hiring our childcare teachers here at Training Wheels Childcare.
What Characteristics Does a Great Childcare Teacher Have?
- Passion for Children
A great childcare teacher genuinely loves working with children and is passionate about their well-being, growth, and development.
- Patience
Working with young children requires a lot of patience and understanding. Great childcare teachers remain calm and composed even in challenging situations.
- Nurturing and Caring
They are nurturing and caring individuals who create a warm and supportive environment where children feel safe, loved, and valued.
- Knowledge of Child Development
A strong understanding of child development allows childcare teachers to tailor activities and interactions to meet each child’s developmental needs.
- Effective Communication
Great childcare teachers have excellent communication skills, both with children and parents. They can convey information and emotions effectively.

- Creativity
They are creative individuals who can design and implement engaging and age-appropriate activities to stimulate children’s learning and imagination.
- Flexibility
Childcare teachers must be adaptable and flexible, as every day with young children can bring surprises and changes in plans.
- Problem-Solving Skills
They can think on their feet and find creative solutions to various challenges that may arise during the day.
- Positive Role Model
Great childcare teachers model positive behavior and attitudes for children to emulate.
- Ability to Build Relationships
They build strong and positive relationships with each child, fostering a sense of trust and security.
- Empathy and Emotional Intelligence
Great childcare teachers understand and empathize with children’s feelings, helping them develop emotional intelligence and social skills.
- Observational Skills
They have keen observational skills, which help them identify each child’s strengths, interests, and areas for growth.
- Team Player
In childcare settings, teamwork is essential. Great childcare teachers work well with colleagues, collaborating to create a harmonious environment for the children.

- Lifelong Learner
A commitment to continuous learning and professional development helps childcare teachers stay up-to-date with best practices and new educational techniques.
- Respectful and Inclusive
They treat every child with respect, dignity, and inclusivity, embracing diversity and celebrating differences.
- Safety Conscious
Great childcare teachers prioritize children’s safety and take necessary precautions to ensure a secure environment.
- Sense of Humor
A sense of humor goes a long way in engaging children and creating a positive atmosphere in the childcare setting.
Childcare teachers play a significant role in shaping a child’s early experiences and development. Their dedication, compassion, and expertise contribute to fostering a love of learning and setting a strong foundation for future success.
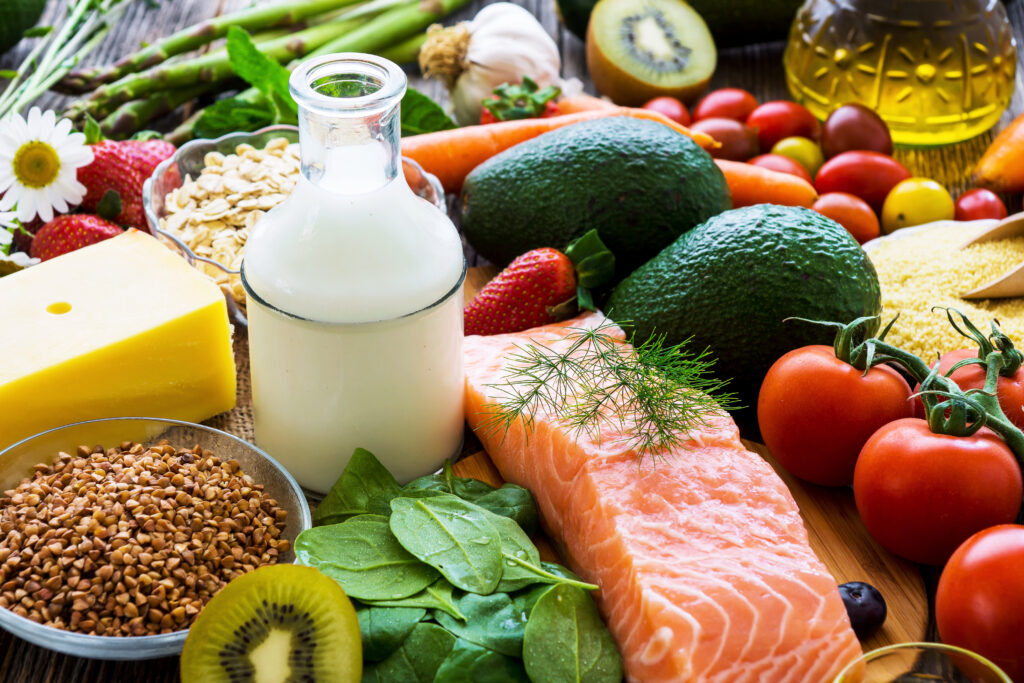
Everything You Need to Know About Childhood Nutrition
Childhood nutrition is crucial for supporting growth, development, and overall health during the early years of life. Here’s everything you need to know about childhood nutrition:
- Balanced Diet
A balanced diet for children includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups. It should consist of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy or dairy alternatives.
- Nutrient Intake
Children require essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats, to support their growth and development.

- Age-Appropriate Servings
Portion sizes should be appropriate for a child’s age and appetite. Younger children typically require smaller portions than older children or adults.
- Breastfeeding or Formula Feeding
For infants, breastfeeding is recommended as the primary source of nutrition for the first six months of life. If breastfeeding is not possible, infant formula is a suitable alternative.
- Introduction of Solid Foods
Solid foods are usually introduced around six months of age, as infants’ nutrient needs outgrow what breast milk or formula alone can provide.

- Introducing a Variety of Foods
Offer a wide range of foods to expand your child’s palate and encourage healthy eating habits. Introducing different flavors and textures early on can help prevent picky eating later.
- Limit Added Sugars and Salt
Limit the consumption of foods and beverages high in added sugars and excessive salt. Instead, focus on natural sources of sweetness, like fruits.
- Hydration
Encourage your child to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially in hot weather or during physical activity.

- Family Meals
Eating together as a family can positively impact a child’s eating habits and social development. It allows children to observe healthy eating behaviors and fosters a sense of connection.
- Snacks
Provide nutritious snacks that complement meals and help meet your child’s energy needs. Opt for fruits, vegetables, whole-grain crackers, or yogurt as healthy snack options.
- Growth Monitoring
Regularly monitor your child’s growth and development through well-child visits with a pediatrician. Growth charts help track your child’s progress and ensure they are growing appropriately.
- Special Dietary Needs
If your child has specific dietary needs or food allergies, consult with a pediatrician or a registered dietitian for guidance on meeting their nutritional requirements.
- Limiting Screen Time
Minimize screen time during meals to promote mindful eating and reduce distractions.
Remember that each child’s nutritional needs may vary based on factors such as age, growth rate, activity level, and overall health.
Consulting with a pediatrician or a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on meeting your child’s specific nutritional needs. Creating a positive and healthy food environment from an early age sets the foundation for a lifetime of good eating habits and well-being.
What are the Benefits of Educational Toys for Infants and Toddlers?
Educational toys offer a range of benefits for infants and toddlers by promoting their cognitive, physical, social, and emotional development.
Here are some key benefits of educational toys for infants and toddlers:
- Cognitive Development
Educational toys stimulate cognitive skills by encouraging exploration, problem-solving, and critical thinking. They can help infants and toddlers develop their sensory perception, object recognition, cause-and-effect understanding, and spatial awareness.
- Fine and Gross Motor Skills
Many educational toys provide opportunities for infants and toddlers to practice and refine their fine and gross motor skills. Manipulating objects, grasping, stacking, sorting, and pushing/pulling toys help develop hand-eye coordination, finger dexterity, balance, and coordination.

- Language and Communication
Educational toys often incorporate elements that promote language and communication development. Toys with buttons, sounds, or labels can help infants and toddlers learn vocabulary, practice early language skills, and enhance their ability to express themselves.
- Social and Emotional Skills
Certain educational toys facilitate social interaction and emotional development. Toys that encourage sharing, turn-taking, cooperation, and role-playing can help children develop empathy, communication skills, and the ability to understand and express emotions.
- Creativity and Imagination
Many educational toys foster creativity and imagination. Toys that allow open-ended play, such as building blocks, art materials, or pretend play sets, encourage infants and toddlers to think creatively, problem-solve, and engage in imaginative play scenarios.
- Sensory Stimulation
Educational toys often provide sensory stimulation, which is crucial for infants and toddlers’ brain development. Toys with different textures, colors, sounds, and shapes engage multiple senses, promoting sensory exploration and integration.
- Focus and Concentration
Certain educational toys can enhance a child’s ability to focus and concentrate. Puzzles, building sets, and activities that require sustained attention and problem-solving promote the development of these skills.

- Self-Confidence and Independence
As infants and toddlers successfully interact with educational toys and achieve goals, it boosts their self-confidence and sense of accomplishment. Toys that allow for independent play and exploration help develop a sense of autonomy and build self-esteem.
- Parent-Child Bonding
Playing with educational toys together provides opportunities for parents and caregivers to bond with their infants and toddlers. Joint play enhances the parent-child relationship, promotes communication, and creates positive experiences.
It’s important to choose age-appropriate educational toys that match the developmental stage and interests of infants and toddlers. Safety is also crucial, so always ensure the toys are free of small parts and meet safety standards. By providing access to quality educational toys, you can support your child’s holistic development and make learning a fun and engaging experience.
Social-Emotional Skills that Young Children Need to Learn
Young children need to develop a range of social-emotional skills to navigate their world and build healthy relationships. Here are some key social-emotional skills that are important for young children to learn:
- Emotional Awareness
Children should learn to identify and understand their own emotions. They need to recognize and label emotions like happiness, sadness, anger, fear, and frustration. This skill helps them understand and express their feelings appropriately.
- Empathy
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. Children should learn to recognize

and respond to the emotions of their peers, siblings, and caregivers. Teaching empathy helps children develop compassion, kindness, and the ability to take the perspective of others.
- Self-Regulation
Self-regulation involves managing and controlling one’s emotions, impulses, and behaviors. Children need to learn strategies for calming themselves when upset, delaying gratification, and adapting to different situations. Self-regulation helps them develop self-control, patience, and resilience.
- Social Skills
Social skills are crucial for building positive relationships and interacting effectively with others. Children should learn skills such as sharing, taking turns, listening, following instructions, cooperating, and resolving conflicts peacefully. These skills foster positive interactions, teamwork, and effective communication.
- Problem-Solving
Problem-solving skills enable children to identify challenges, think critically, and find solutions. They need to learn how to approach problems, generate alternative solutions, evaluate options, and make decisions. Problem-solving skills promote independence, critical thinking, and resilience.
- Self-Esteem and Self-Confidence

- Respect and Empowerment
Children should learn to respect themselves, others, and the environment. They need to understand the value of diversity, inclusivity, and treating others with kindness and fairness. Empowering children involves giving them a sense of autonomy, encouraging their voice and choices, and promoting their sense of worth.
- Resilience
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from setbacks, adapt to change, and cope with challenges. Children should learn strategies to manage stress, cope with disappointments, and persevere through difficulties. Building resilience helps children develop a growth mindset, optimism, and a positive attitude toward challenges.
These social-emotional skills are interrelated and play a vital role in children’s overall development. Parents, caregivers, and educators can support the development of these skills through nurturing relationships, modeling positive behaviors, providing guidance and support, and creating environments that foster social-emotional growth.
10 Ways You Can Help Your Child Cope with Separation
Every child will deal with separation anxiety at some point, and it can be a really tough time for both the kids and their parents. While it might seem like there is nothing you can do, there are some strategies you can implement to help your child cope with their separation anxiety.
Just keep in mind that helping a child cope with separation is a gradual and supportive process. Take your time with them and be gentle as you apply the following strategies.
How Can You Help Your Child Cope with Separation?
- Prepare and Provide Information
Talk to your child in advance about the upcoming separation, whether it’s a short-term separation (such as going to school or daycare) or a longer-term separation (such as a parent’s work trip). Explain where you will be and when you will return, using concrete terms they can understand.
- Establish Routines and Consistency
Consistent routines can provide a sense of stability and security for your child. Set up predictable daily routines that your child can rely on, which can help alleviate anxiety and make separations easier to manage.
- Practice Gradual Separations
Gradually introduce short separations to help your child build confidence and trust in your return. Start with brief separations and gradually increase the duration as your child becomes more comfortable.

- Create a Goodbye Ritual
Establish a consistent and positive goodbye routine. This could involve a special hug, a reassuring phrase, or a small item (such as a family photo) that your child can keep with them during the separation. A routine helps provide a sense of predictability and security.
- Encourage Connections with Caregivers
Help your child develop a positive relationship with the caregivers they will spend time with during the separation. Encourage interactions, playdates, and conversations to build familiarity and trust.
- Stay Connected
When possible, maintain regular communication with your child during the separation. This can include phone calls, video chats, or exchanging drawings or letters. Knowing that you are still connected can provide reassurance and help ease any anxiety they may feel.
- Validate Feelings
Acknowledge and validate your child’s emotions about the separation. Let them know that it’s normal to feel sad or worried when apart and reassure them that you understand their feelings. Provide a safe space for them to express their emotions and offer comfort and support.

- Model Resilience
Show your child that you can cope with separations positively. Demonstrate confidence and optimism about your return. Seeing you handle separations in a calm and confident manner can help your child feel more secure.
- Involve Your Child in the Process
Give your child a sense of control and involvement by allowing them to contribute to the separation process. For example, they can help pack a small bag or choose a special item to bring with them.
- Seek Support When Needed
If your child continues to struggle with separation anxiety or if the anxiety becomes severe, consider seeking guidance from a pediatrician, therapist, or child development specialist who can provide further support and guidance.
Remember that each child is unique, and the process of coping with separation may vary. Be patient, understanding, and supportive as your child gradually learns to manage separations more independently.
The Importance of Knowing Infant and Child CPR
It’s important for parents and caretakers alike to know how to perform infant and child CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation). Knowing these skills are of the utmost importance for several reasons.
The Importance of Knowing Infant and Child CPR
- Life-Saving Skills
Infant and child CPR can save lives in emergency situations. By knowing how to perform CPR correctly, you can provide immediate assistance to an infant or child who is experiencing cardiac or respiratory arrest.
- Immediate Response
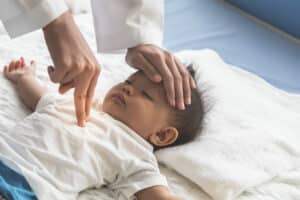
- Accidents and Emergencies
Infants and children are prone to accidents and emergencies such as choking, drowning, or sudden cardiac events. Being trained in CPR equips you with the skills to respond appropriately in such situations, potentially preventing further harm or even death.
- Peace of Mind
Having the knowledge and confidence to perform CPR can provide peace of mind for parents, caregivers, and anyone responsible for the well-being of infants and children. It helps alleviate anxiety and allows you to take immediate action during emergencies.
- Enhanced Safety
Knowing CPR not only benefits the children in your care but also makes the overall environment safer. When more people are trained in CPR, the chances of a timely response and successful resuscitation increase, making communities safer for infants and children.
- Preparedness

CPR training goes beyond just learning the techniques. It often includes education on recognizing signs of distress, understanding common risks, and implementing preventive measures. This preparedness mindset helps create a safer environment for infants and children.
- Advocacy for Child Safety
By knowing infant and child CPR, you become an advocate for child safety. You can share your knowledge with others, raise awareness about the importance of CPR, and encourage others to undergo CPR training as well.
Remember that infant and child CPR techniques differ from adult CPR due to anatomical and physiological differences. It is crucial to receive proper training and certification in infant and child CPR to ensure you are equipped with the right skills and knowledge.
